Difference between revisions of "Geometry Functions"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Geometry Functions is a very rich tool. How it works depends highly on the geometry function you choose : | Geometry Functions is a very rich tool. How it works depends highly on the geometry function you choose : | ||
| − | * '''Geometry functions using a mask''' - A mask is a layer containing a single geometry. The following functions will compare each geometry of the source layer to the mask. Note that the single geometry contained in the mask may be a MultiGeometry but not a GeometryCollection. The result contains as many features as the source layer. | + | * '''Geometry functions using a layer and a mask''' - A mask is a layer containing a single geometry. The following functions will compare each geometry of the source layer to the mask. Note that the single geometry contained in the mask may be a MultiGeometry but not a GeometryCollection. The result contains as many features as the source layer. |
** ''Intersections'' - Creates features which are the intersection of source feature geometries with the mask. | ** ''Intersections'' - Creates features which are the intersection of source feature geometries with the mask. | ||
** ''Union'' - Creates features which are the union of each single feature of source layer with the feature geometry of mask. | ** ''Union'' - Creates features which are the union of each single feature of source layer with the feature geometry of mask. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
** ''Difference (B-A)'' - You may want to do the opposite : remove feature geometries from ocean area. | ** ''Difference (B-A)'' - You may want to do the opposite : remove feature geometries from ocean area. | ||
** ''Symmetric difference'' - Symmetric difference will keep the part of source geometries which does not intersect the mask with the part of the mask which does not intersects the source geometry. | ** ''Symmetric difference'' - Symmetric difference will keep the part of source geometries which does not intersect the mask with the part of the mask which does not intersects the source geometry. | ||
| + | * '''Geometry functions using a single layer''' | ||
| + | ** ''Centroid of A'' - Computes the centroid of each feature geometry. The centroid is equal to the centroid of the set of component Geometries of highest dimension (since the lower-dimension geometries contribute zero "weight" to the centroid). | ||
| + | ** ''Interior Point'' | ||
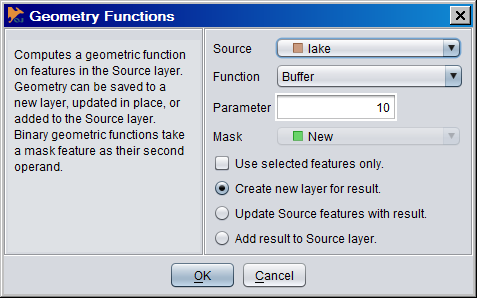
| + | ** ''Buffer'' | ||
| + | ** ''Simplify (D-P)'' | ||
| + | ** ''Simplify (Preserve Topology)'' | ||
Revision as of 00:58, 9 July 2011
Geometry Functions is a very rich tool. How it works depends highly on the geometry function you choose :
- Geometry functions using a layer and a mask - A mask is a layer containing a single geometry. The following functions will compare each geometry of the source layer to the mask. Note that the single geometry contained in the mask may be a MultiGeometry but not a GeometryCollection. The result contains as many features as the source layer.
- Intersections - Creates features which are the intersection of source feature geometries with the mask.
- Union - Creates features which are the union of each single feature of source layer with the feature geometry of mask.
- Difference (A-B) - Substract geometry of the mask to each feature of the source layer. You can for example clean a layer by removing parts of feature geometries overlapping the ocean surface..
- Difference (B-A) - You may want to do the opposite : remove feature geometries from ocean area.
- Symmetric difference - Symmetric difference will keep the part of source geometries which does not intersect the mask with the part of the mask which does not intersects the source geometry.
- Geometry functions using a single layer
- Centroid of A - Computes the centroid of each feature geometry. The centroid is equal to the centroid of the set of component Geometries of highest dimension (since the lower-dimension geometries contribute zero "weight" to the centroid).
- Interior Point
- Buffer
- Simplify (D-P)
- Simplify (Preserve Topology)